Insulated siding cost per square foot is a crucial factor when planning a home exterior renovation. Understanding the variables influencing this cost, from material selection and regional differences to labor expenses and installation complexity, is key to accurate budgeting. This exploration delves into the specifics, providing a clear picture of what homeowners can expect to pay and how to make informed decisions.
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of insulated siding costs, breaking down the factors that influence pricing and offering practical advice for budgeting and finding reliable contractors. We’ll explore various siding materials, compare costs with traditional siding, and address common concerns homeowners have when undertaking such a project. The goal is to equip you with the knowledge necessary to confidently navigate the process of upgrading your home’s exterior.
Factors Affecting Insulated Siding Cost
The cost of insulated siding is influenced by a variety of factors, extending beyond simply the material itself. Understanding these factors is crucial for accurate budgeting and informed decision-making during a home renovation or new construction project. This section details the key elements that contribute to the overall price per square foot.
Material Type and Cost
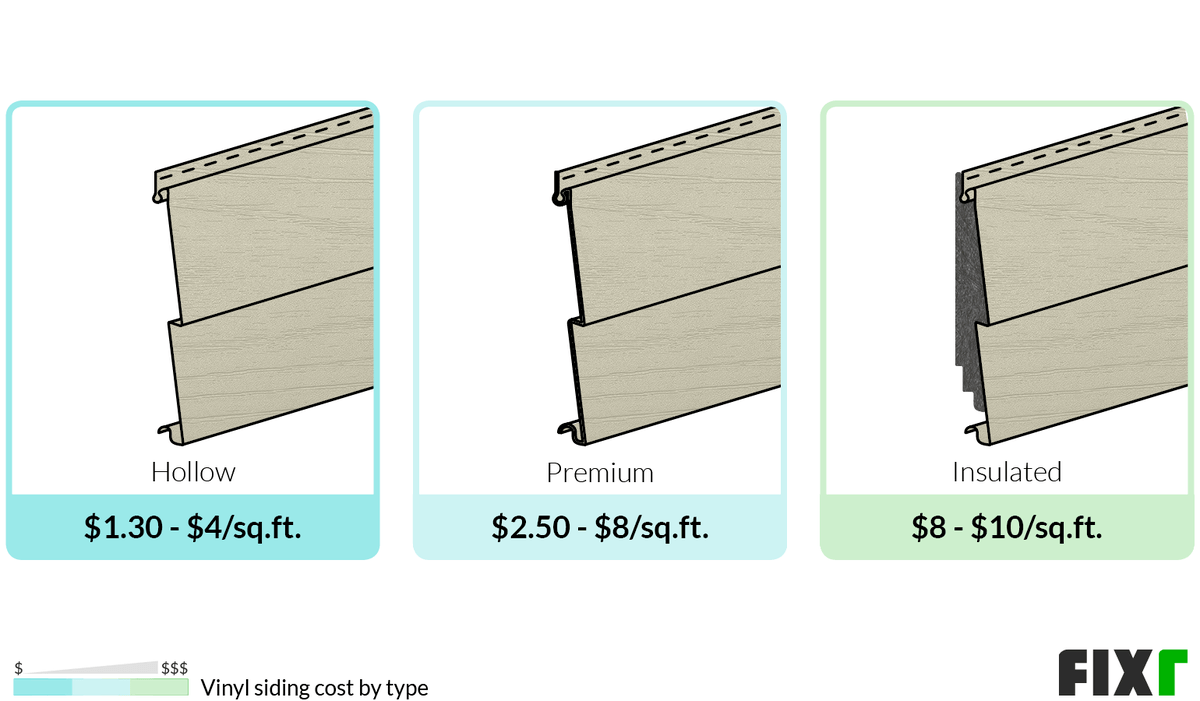
The material chosen significantly impacts the cost. Vinyl siding, a popular and relatively inexpensive option, generally ranges from $3 to $12 per square foot, including installation. Fiber cement siding, known for its durability and aesthetic appeal, typically costs between $8 and $20 per square foot installed. Metal siding, while offering exceptional longevity and weather resistance, is often the most expensive, ranging from $10 to $30 or more per square foot installed. These price ranges reflect variations in quality, thickness, and finish options available within each material category.
Siding Thickness and R-Value
Thicker siding generally provides better insulation and, consequently, a higher R-value (a measure of thermal resistance). A higher R-value translates to improved energy efficiency and lower heating and cooling costs over the life of the siding. However, thicker siding and higher R-values also tend to increase the initial cost per square foot. For example, a vinyl siding with an R-value of 4 might cost less than a fiber cement option with an R-value of 6, even if the latter has a lower square footage cost for the material itself. This highlights the importance of considering the long-term cost savings associated with better insulation.
Labor Costs and Installation Complexity
Labor costs constitute a substantial portion of the overall expense. Installation complexity significantly influences labor hours and, therefore, the final price. Simple, flat-surface installations require less time and labor than projects involving intricate detailing, multiple angles, or significant repairs to underlying sheathing. Furthermore, labor rates vary considerably based on geographical location. Highly skilled installers in densely populated urban areas typically command higher wages than those in less populated regions.
Regional Differences in Material and Labor Costs
Regional variations in material availability and labor rates substantially impact the final cost. Areas with limited access to specific siding materials might experience higher prices due to transportation and distribution costs. Similarly, regions with a higher cost of living or a shortage of skilled installers will likely have elevated labor rates, leading to increased overall project expenses. For instance, a project in a coastal area might incur higher costs for both materials (due to potential shipping challenges) and labor (due to higher demand and competition).
Insulated Siding Material Cost Comparison
| Material | Cost Range ($/sq ft installed) | Typical R-Value | Lifespan (Years) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vinyl | $3 – $12 | 3-5 | 20-50 |
| Fiber Cement | $8 – $20 | 4-8 | 50-80 |
| Metal | $10 – $30+ | Variable, often higher with added insulation | 50+ |
Estimating Insulated Siding Costs
Accurately estimating the cost of insulated siding involves several key steps, from calculating the square footage of your home’s exterior walls to accounting for potential cost overruns. A well-prepared estimate ensures a smooth and financially responsible project.
Calculating Exterior Wall Square Footage
Determining the square footage of your home’s exterior walls is the foundation of any accurate cost estimate. This involves measuring the length and height of each wall, then multiplying those dimensions to find the area of each wall. Remember to subtract the area of any windows and doors. For complex shapes or multiple stories, consider breaking the house down into smaller, easily measurable sections. For example, a simple rectangular house can be easily calculated by measuring the length and height of each side and adding the totals. Houses with more complex designs might require more detailed measurements and potentially the assistance of a professional estimator. Always double-check your measurements to minimize errors.
Estimating Total Material Costs
Once you have the total square footage of your exterior walls, estimating material costs is straightforward. Obtain quotes from several siding suppliers, noting the price per square foot for the chosen insulated siding material. Multiply the total square footage by the price per square foot to determine the total material cost. Remember to factor in any additional materials, such as trim, flashing, and fasteners. For instance, if your total square footage is 1500 square feet and the cost per square foot of vinyl insulated siding is $8, the material cost would be $12,000 (1500 sq ft * $8/sq ft). Always get multiple quotes to ensure you’re getting a competitive price.
Common Cost Overruns and Mitigation Strategies
Unexpected costs are a common occurrence in home improvement projects. Some frequent cost overruns for insulated siding installations include unforeseen damage to existing siding requiring additional repairs, unexpected complexities in the underlying wall structure requiring extra labor, and changes to the scope of the project requested by the homeowner. To mitigate these risks, conduct a thorough inspection of the existing siding before starting the project, and have detailed discussions with your contractor about potential complications and their associated costs. Getting multiple detailed quotes upfront allows for better comparison and helps in identifying potential cost overruns. Clearly define the scope of work in a written contract to avoid misunderstandings and extra expenses.
Sample Cost Estimate for a 1500 Square Foot House
This sample estimate uses average pricing for vinyl insulated siding in a mid-range market. Actual costs can vary depending on location, labor rates, and material choices.
- Material Costs: $12,000 (1500 sq ft x $8/sq ft for vinyl insulated siding)
- Labor Costs: $6,000 – $9,000 (This is a range, depending on labor rates and project complexity)
- Permit Costs: $500 – $1,500 (This varies greatly depending on location and permit requirements)
- Contingency/Unexpected Costs: $1,500 – $3,000 (10-20% of total estimated cost to account for unforeseen issues)
- Total Estimated Cost: $21,000 – $25,500 (This represents a range based on the variables above)
Insulated Siding vs. Traditional Siding
Choosing between insulated and traditional siding involves a careful consideration of upfront costs versus long-term energy savings. While insulated siding commands a higher initial investment, its superior energy efficiency can lead to significant cost reductions over the lifespan of the siding. This comparison explores the financial implications of each option, highlighting the potential return on investment for insulated siding.
Long-Term Cost-Effectiveness Comparison
The long-term cost-effectiveness of insulated siding hinges on its ability to reduce energy consumption. Traditional siding, lacking insulation, forces your heating and cooling systems to work harder, leading to higher energy bills. Insulated siding, on the other hand, acts as a thermal barrier, minimizing heat transfer and thus reducing the load on your HVAC system. This translates to lower energy bills and a potentially faster return on the higher initial investment.
Energy Savings with Insulated Siding Over 10 Years
The potential energy savings associated with insulated siding can vary greatly depending on factors such as climate, home size, insulation R-value, and energy prices. However, we can illustrate potential savings with a hypothetical example. Let’s assume a typical suburban home with 1500 square feet of exterior wall space. Switching from traditional vinyl siding to insulated vinyl siding with an R-value of 4 could result in a 10-15% reduction in heating and cooling costs. Assuming an average annual energy bill of $2000, this translates to savings of $200-$300 per year. Over a 10-year period, this amounts to $2000-$3000 in savings. These savings can significantly offset the higher initial cost of insulated siding.
Impact of Different Insulation Levels on Energy Savings
The level of insulation in the siding directly impacts its energy-saving capabilities. Higher R-values indicate better insulation. For instance, insulated siding with an R-value of 6 will generally offer greater energy savings than siding with an R-value of 4. To illustrate, consider a home in a colder climate. The higher R-value siding might reduce heating costs by 20%, compared to 15% for the lower R-value siding. This difference, while seemingly small, can accumulate to substantial savings over the long term, potentially justifying the increased upfront cost.
Twenty-Year Cost Comparison: Insulated vs. Traditional Siding
The following table compares the estimated costs over 20 years, considering both initial investment and energy savings. These figures are hypothetical and will vary depending on location, material costs, and energy prices.
| Siding Type | Initial Cost | Long-Term Energy Savings (20 years) | Total Cost of Ownership (20 years) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Vinyl Siding | $8,000 | $0 | $8,000 |
| Insulated Vinyl Siding (R-4) | $12,000 | $3,000 | $9,000 |
| Insulated Vinyl Siding (R-6) | $14,000 | $5,000 | $9,000 |
Visual Representation of Cost Differences
The visual appeal of insulated siding significantly impacts a homeowner’s decision, often outweighing purely cost-based considerations. Understanding the visual differences between various materials and installation styles helps in appreciating the cost variations. Different materials offer unique textures, colors, and profiles, all contributing to the overall aesthetic and, consequently, the price.
Different insulated siding materials present a wide array of visual possibilities. The texture can range from the smooth, almost glassy finish of certain vinyl sidings to the deeply textured, wood-like appearance of some fiber cement options. Color palettes are equally diverse, encompassing a spectrum from classic earth tones and muted grays to bold, vibrant hues. The subtle variations in color and sheen can dramatically alter the perceived value and overall cost.
Insulated Siding Material Appearances
The visual impact of various insulated siding materials is substantial. For instance, imagine a home clad in smooth, white vinyl siding. Its clean, modern look is easily achievable and generally reflects a lower price point compared to more complex materials. In contrast, picture a home featuring deeply textured, dark gray fiber cement siding. This evokes a feeling of rustic elegance and often commands a higher price due to the material’s inherent quality and the potentially more intricate installation process. Similarly, engineered wood siding might present a natural wood grain appearance, with subtle color variations and a more rustic feel, reflecting a mid-range price point between vinyl and fiber cement.
Siding Profile and Aesthetic Impact
The profile of the siding—its shape and how it’s installed—significantly influences the home’s aesthetic. A simple, flat panel siding provides a clean, contemporary look, often seen in more budget-friendly options. More complex profiles, such as clapboard or shingle styles, add visual interest and often contribute to a higher perceived value and cost. The interplay of light and shadow on these varied profiles also creates depth and texture, enhancing the overall curb appeal.
High-Quality Insulated Siding Installations
Consider an image depicting a home with a high-quality installation of dark brown, cedar-shake style fiber cement siding. The deep, rich color contrasts beautifully with the crisp white trim. The individual shakes are meticulously aligned, creating a uniform, yet natural-looking surface. The installation shows attention to detail, with precise cuts and consistent spacing between the shakes, highlighting the superior craftsmanship reflected in the higher cost. Now, imagine a different image showcasing a light gray, smooth vinyl siding installation on a craftsman-style home. The clean lines of the siding complement the home’s architectural style. The uniform color and smooth surface create a sleek, modern aesthetic, showcasing a more economical yet still visually appealing choice. A third image might portray a home with a charming, light beige engineered wood siding, showcasing the natural wood grain and texture. The siding is installed with precision, showcasing the individual planks and their subtle variations in color, creating a warm, inviting look that reflects a mid-range price point.
Finding Reliable Contractors for Insulated Siding Installation
Choosing the right contractor is crucial for a successful insulated siding installation. A reputable contractor ensures quality workmanship, adheres to timelines, and provides excellent customer service, ultimately protecting your investment. Careless selection can lead to costly repairs, delays, and significant frustration.
Selecting a qualified contractor involves several key steps to minimize risk and maximize the value of your project. This includes thorough research, comparison shopping, and verification of credentials.
Contractor Qualification Verification
Verifying a contractor’s qualifications protects you from potential problems. This involves checking their licensing, insurance coverage, and reviewing online reviews and testimonials. A licensed and insured contractor demonstrates a commitment to professional standards and provides financial protection in case of accidents or disputes. For example, you can check your state’s contractor licensing board website to confirm a contractor’s license is valid and up-to-date. Similarly, requesting proof of liability and workers’ compensation insurance protects you from potential financial liability if an accident occurs on your property. Examining online reviews on platforms like Yelp or Google Reviews offers insights into past clients’ experiences with the contractor, revealing their professionalism, responsiveness, and the quality of their work.
Obtaining and Comparing Multiple Bids
Getting at least three bids from different contractors is essential for informed decision-making. This allows for a comprehensive comparison of pricing, materials, and services offered. Each bid should detail the scope of work, materials to be used, payment schedule, and warranty information. For example, one contractor might offer a slightly higher price but use superior materials with a longer warranty, while another might offer a lower price but use lower-quality materials. Comparing these factors allows you to determine the best value for your investment. Differences in pricing can be substantial, often exceeding 10-20% depending on the contractor’s experience, overhead, and materials used.
Questions to Ask Potential Contractors
Asking specific questions helps you assess a contractor’s experience, understanding of the project, and commitment to customer satisfaction. This proactive approach minimizes misunderstandings and ensures alignment of expectations. Examples of pertinent questions include: “Can you provide references from recent projects similar to mine?”, “What is your process for handling unexpected issues or changes during the installation?”, “What type of warranty do you offer on your workmanship and materials?”, and “What is your timeline for completing the project?”. Thorough questioning reveals a contractor’s professionalism, attention to detail, and their ability to handle potential challenges effectively.
Summary
Ultimately, the cost of insulated siding per square foot is highly variable, dependent on a multitude of factors. However, by carefully considering material choices, regional pricing, and labor costs, homeowners can develop realistic budgets and make informed decisions that align with their financial goals and aesthetic preferences. Remember that investing in high-quality insulated siding can lead to significant long-term energy savings, making it a worthwhile investment for increased comfort and reduced utility bills.